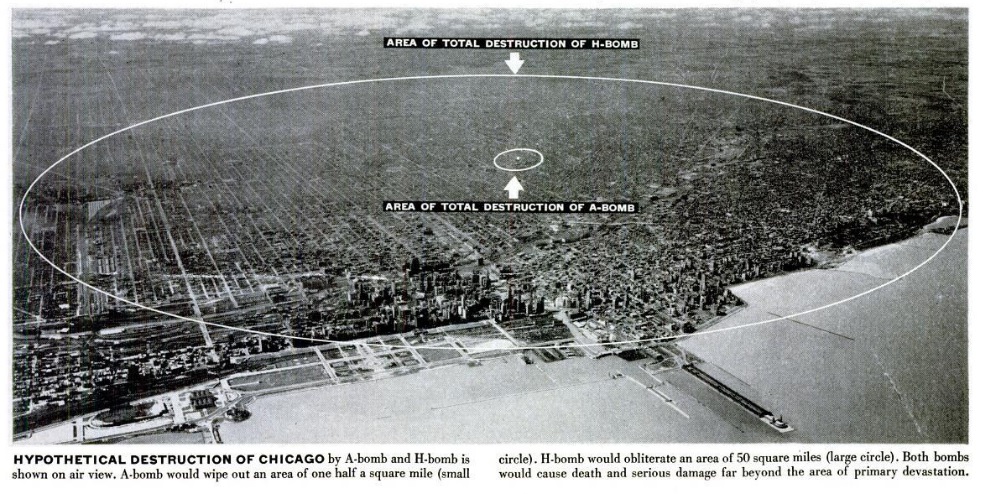
 The first hydrogen bomb wasn’t tested until 1952, but two years earlier, readers of Life Magazine, January 30, 1950, got a pretty good idea of what it would be capable of. The above picture shows the blast radius for the A-bomb (small circle) compared to that of the H-bomb (large circle).
The first hydrogen bomb wasn’t tested until 1952, but two years earlier, readers of Life Magazine, January 30, 1950, got a pretty good idea of what it would be capable of. The above picture shows the blast radius for the A-bomb (small circle) compared to that of the H-bomb (large circle).
Colorado Senator Edwin C. Johnson had referenced the new bomb in a television broadcast, the press followed up, and President Truman had failed to either confirm or deny that the project was underway. The magazine noted that the nation was still trying to adjust itself to life with the A-bomb, but the new bomb, which would harness the same energy as the sun itself, would make the Hiroshima weapon look like a stick of dynamite.