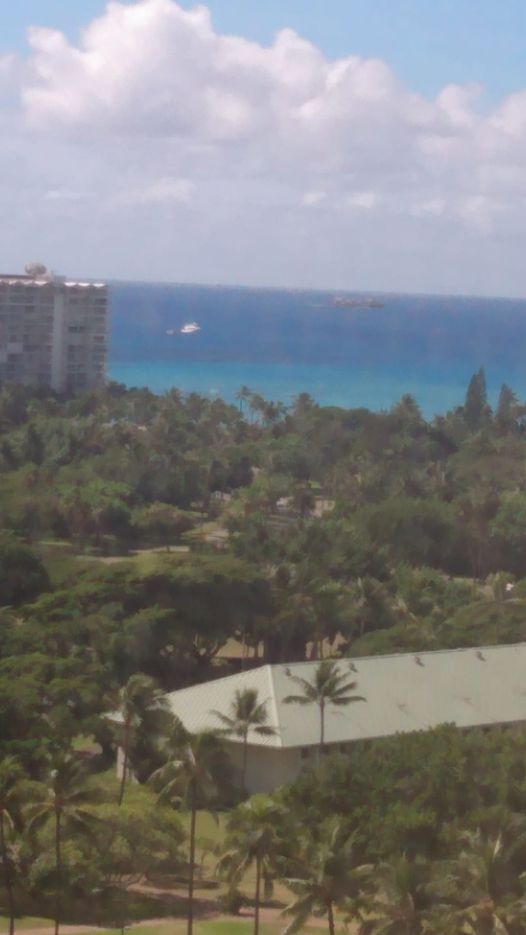
As we previously reported, we were in Hawaii for the sunrise eclipse of October 2, 2024. Unfortunately, we were clouded out, but we still enjoyed a nice visit to the Aloha State.
As we previously reported, we were in Hawaii for the sunrise eclipse of October 2, 2024. Unfortunately, we were clouded out, but we still enjoyed a nice visit to the Aloha State.
Of course, Hawaii can be expensive, and we wanted to share some budget vacation travel tips. We decided to stay in Honolulu, on the Island of Oahu, so the first order of business was buying the flights to get there. I kept checking a number of sites for several days, watching prices go up and down, and I also checked departures from various cities. We flew from Minneapolis. We could have saved some money by flying from Chicago and driving there. But after the added cost of driving there and finding a place to park, it wound up being a wash. Eventually, we paid about $450 per person on Priceline, and had an excellent flight on United, with connections in Denver. According to Priceline, our tickets were limited to a “personal item” rather than a full “carry on” baggage item. But when we called United, were were assured that we could take both a personal item and a carryon. In addition, we booked a couple of checked baggage items for about $30 each, directly with United.
Lodging
 Lodging options work differently in Hawaii than in the Continental U.S. My go-to source for hotel rooms is Hotels.com, and I can usually find a bargain. This time, I wound up using Priceline again, and the same room shown (not the same type of room, but the same exact room) was considerably cheaper on Priceline, so that’s how I booked it. The majority of the lower priced options are not actually hotels, but actually condos. The one I booked was actually located within a hotel, but it was owned separately. So, for better or worse, there was no front desk to deal with. We received instructions on retrieving the room key from a lockbox in the lobby. If we had concerns with the room, we could call or e-mail. We had few issues, but they were resolved promptly. For example, the coffee maker didn’t work, and (after a couple of calls), the delivered a new one. The property was managed by a company called Red Awning. While we never actually saw anyone from that company in person, we were satisfied. The view from our window is shown at the top of this page. We were on the 21st floor of the hotel. Specifically, we were in Room 2108 of the Hawaiian Monarch hotel, about six blocks from the Waikiki beach.
Lodging options work differently in Hawaii than in the Continental U.S. My go-to source for hotel rooms is Hotels.com, and I can usually find a bargain. This time, I wound up using Priceline again, and the same room shown (not the same type of room, but the same exact room) was considerably cheaper on Priceline, so that’s how I booked it. The majority of the lower priced options are not actually hotels, but actually condos. The one I booked was actually located within a hotel, but it was owned separately. So, for better or worse, there was no front desk to deal with. We received instructions on retrieving the room key from a lockbox in the lobby. If we had concerns with the room, we could call or e-mail. We had few issues, but they were resolved promptly. For example, the coffee maker didn’t work, and (after a couple of calls), the delivered a new one. The property was managed by a company called Red Awning. While we never actually saw anyone from that company in person, we were satisfied. The view from our window is shown at the top of this page. We were on the 21st floor of the hotel. Specifically, we were in Room 2108 of the Hawaiian Monarch hotel, about six blocks from the Waikiki beach. 
We paid about $150 per night for this room. This brings us to the first point about booking hotels in Hawaii: Make sure that the price you are quoted is the complete price. On Priceline, we paid Priceline directly, and there were no other fees. On some websites, and perhaps at other hotels, there is a “resort fee” or similar language tacked on, and you need to pay this later. So check the total price, and make sure there are no extras.
Our room was quite adequate, although it’s quite a bit smaller than the pictures on the booking websites make it look. But for a home base during our stay, it met our needs. Keep in mind that, unlike a hotel, there is no housekeeping. You’ll probably need to do laundry to wash your towels. There was a reasonably priced laundry in the building (and don’t forget to buy some laundry detergent at Walmart–see below). There was a swimming pool, and even an outdoor picnic area poolside with gas grills for guests to use. Overall, we were pleased with the accommodations.
Camping
 With high prices, the budget-conscious traveler might be tempted to think about camping, and I looked into the option. But they make it difficult, for a few reasons.
With high prices, the budget-conscious traveler might be tempted to think about camping, and I looked into the option. But they make it difficult, for a few reasons.
First of all, Hawaii has some very nice state parks, and they are fairly reasonably priced. But they cleverly make them hard to camp in for long stays. The state parks are closed on Wednesday and Thursday nights! If you’re going to be there five days, make sure you arrive Thursday morning and leave Wednesday. But for those two nights, you’ll need to find somewhere else to stay. And it won’t be camping, because there are few, if any, other campgrounds. You’ll need to pay to stay in a hotel. (On other islands, the National Park campgrounds might offer some options worth looking into.)
Don’t even think about sleeping in your car or camping on the beach. They’ve also thought of that, and the laws against it seem to be enforced very seriously. Also, city parks are posted that they are closed overnight. In some cases, there are gates, but even if there aren’t, those laws also seem to be enforced. If you do find a parking place, parking fees are very expensive. (Parking is an additional fee at most hotels. At ours, it was $40 per night.)
Also, public restrooms are extremely hard to find. Most gas stations don’t have them. At one McDonald’s restaurant, there was no public restroom at all. And at another one, the door was locked, and available only for paying customers.
If you truly are going to be there only five days, you can buy, at fairly normal prices, camping gear at Walmart. So you can bring most items from home, and perhaps buy a cheap tent when you get there. But they do make it difficult to camp, so that’s generally not the budget lodging option it is many other places.
Transportation
 The other problem with camping is that you probably need a car, and the cost of renting a car would probably make hotels a better option. (Although, as noted below, it’s actually possible to get to most or all state park campgrounds by city bus, so if you can haul your gear, that might be an option.)
The other problem with camping is that you probably need a car, and the cost of renting a car would probably make hotels a better option. (Although, as noted below, it’s actually possible to get to most or all state park campgrounds by city bus, so if you can haul your gear, that might be an option.)
That being said, car rentals are fairly reasonably priced. I have nothing but praise for 808SmartCars.com, where we rented a car on two separate days. They were located in our hotel lobby, and in another hotel several blocks away. The total cost was $47 one day, and $68 the other day. (And if it’s only two people, their Smart Cars are even cheaper.) For that price, you get the car for a full 24 hours. One day, we got it the first thing in the morning and returned it late at night. The next time (when we needed it for the sunrise eclipse), we rented it about noon and returned it the next day before noon. In that case, we had to pay for parking at a reduced rate, but we did have in-and-out privileges. Normally, parking, even if you have a hotel room, is very expensive, so it’s best to rent a car only on days when you need it. Mopeds and scooters are also readily available for rent.
Gas was not particularly expensive. I believe it was about a dollar more than in the Continental U.S. But Oahu is relatively small, and we really didn’t burn much gas, and it wasn’t a major concern.
For day to day transportation, the city bus system in Honolulu, TheBus.org, has excellent service. And it doesn’t just cover the city–it covers the entire island of Oahu. So even if you need to get to a rural area, it’s a good option. (If you do decide to camp, and are able to carryparall of your gear, you could easily take the bus to a State Park.) The fare is only $3.00, which covers transfers within 2-1/2 hours. That should get you anywhere on the island. And you will never pay more than $7 per day, no matter how much you ride. To take advantage, you will buy a HOLO card, which you can get at 7-11 and other locations for $2. You can add money at the store, or online.
For example, we took the city bus to visit the Pearl Harbor Memorial. On the way back, we stopped at Target to get a few groceries, and the ride was extremely convenient. You can easily look up routes online, and it’s a very pleasant way to travel.
Food and supplies
Our condo had a small kitchenette. It included a sink, a microwave, a refrigerator, a toaster, a coffee maker, and a hotplate, along with an assortment of utensils. Also, as noted above, we had an outdoor grill available. Eating out is very expensive in Hawaii, even at fast-food restaurants. You will save a small fortune if you prepare most of your meals yourself, to eat in your room, or as a picnic lunch.
 There are many convenience stores, but they all cater to the tourist market, and they are also very expensive. But you can get groceries at a reasonable price at Walmart! Not only do they have stores in Hawaii, but they deliver. I prepared a grocery order online in preparation of our trip. I selected the address of our condo and used my cell phone number. I was then able to prepare an order at the Walmart in downtown Honolulu (specifically 700 Keeaumoku St, Honolulu, HI 96814). When we arrived, I made a few last-minute changes and additions and placed the order. There was a small delivery charge, and I added a tip for the driver. But most of the groceries we needed for a week were delivered at 10:00 PM, and we were all set. That store, as well as Target, was within walking distance of our hotel. On one occasion, we were at Target and got a few things. Walmart prices were better, but Target wasn’t too far out of line. They were both much more reasonable that the convenience stores.
There are many convenience stores, but they all cater to the tourist market, and they are also very expensive. But you can get groceries at a reasonable price at Walmart! Not only do they have stores in Hawaii, but they deliver. I prepared a grocery order online in preparation of our trip. I selected the address of our condo and used my cell phone number. I was then able to prepare an order at the Walmart in downtown Honolulu (specifically 700 Keeaumoku St, Honolulu, HI 96814). When we arrived, I made a few last-minute changes and additions and placed the order. There was a small delivery charge, and I added a tip for the driver. But most of the groceries we needed for a week were delivered at 10:00 PM, and we were all set. That store, as well as Target, was within walking distance of our hotel. On one occasion, we were at Target and got a few things. Walmart prices were better, but Target wasn’t too far out of line. They were both much more reasonable that the convenience stores.
The Walmart where we placed our order was downtown, and didn’t look like a typical Walmart. But in more rural areas, the stores looked like the familiar ones at home. The other supermarket chain that seemed to offer reasonable prices was Foodland.
Some items were considerably more expensive than on the mainland. In particular, bread seemed very expensive. It was about $4 per loaf of the cheap stuff, as opposed to $1.50 at home. Milk was about $6 per gallon, as opposed to $3 at home. Much produce was unavailable or extremely expensive. But canned and dry goods were only slightly higher than at home. This undoubtedly explains why Spam is so popular in Hawaii–it costs about the same as on the mainland, whereas other meats are much more expensive.
The nice thing about ordering online at Walmart is that you can shop around by price long before your trip and make your selections. When you get there, finalize your order, and you’ll have all of your groceries delivered the same day you arrive.